Why are we conducting this survey?
We are undertaking research to gather information on the prosthetic and orthotic workforce in the UK. The study aims to capture a wide variety of demographic and work-related information about the UK prosthetic and orthotic workforce. Currently, workforce data for people working within the prosthetics and orthotics profession is incomplete resulting in an unknown national workforce picture, which prevents accurate service planning and projection requirements. The project has been funded by Health Education England through the British Association of Prosthetists and Orthotists (BAPO). The findings of the study have the potential to influence future service planning.
Who do we want to complete the survey?
We want to gather information on all individuals working within the prosthetic and orthotic profession which includes:
• Prosthetists/Orthotists
• Prosthetic/Orthotic technician
• Prosthetic/Orthotic support worker
• Prosthetic/Orthotic student/apprentice
Survey update
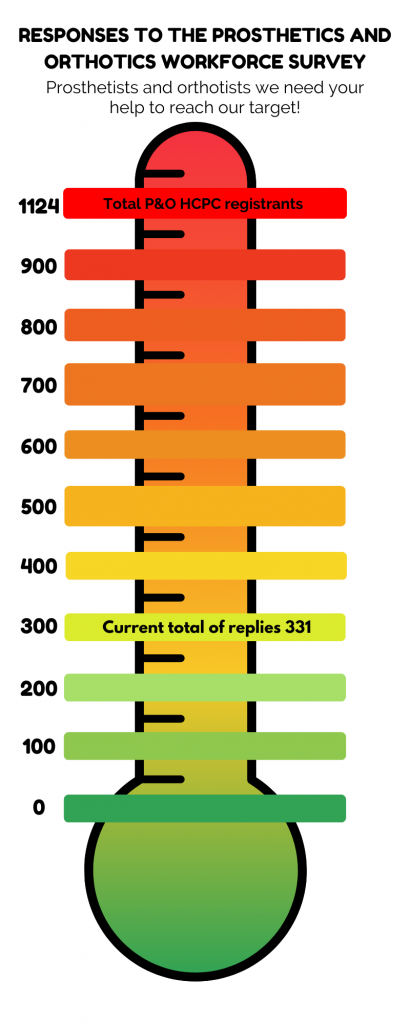
- The survey has now been running for 4 weeks but we need your help to get more responses, from all professions across the UK. We know that there are 1,124 registered Prosthetists/Orthotists in the UK today and so far, we have only had responses from 30% of this population.
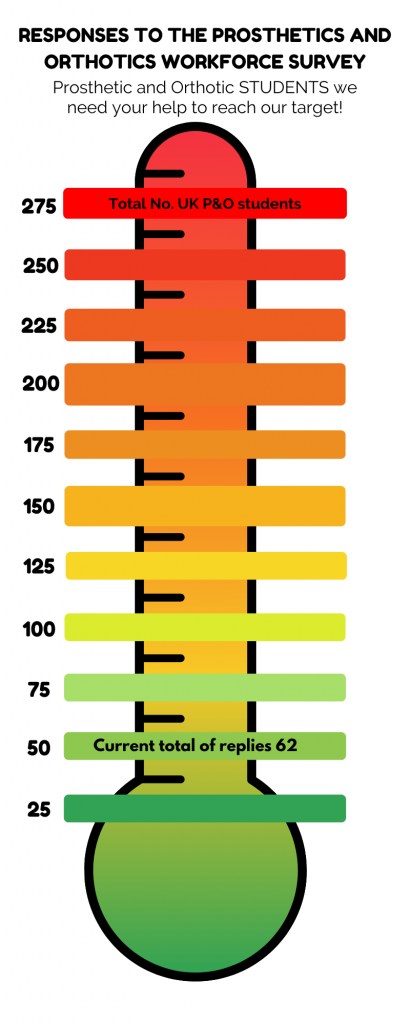
- We have a low response from technicians, support workers, students, and apprentices.
- We have a low response from Northern Ireland, Wales, and Scotland.
To complete the survey, click here or scan the QR code:
There is a chance to win a £100 retail voucher, the survey closes 18/11/22.


